Thinking about going solar? It's about more than just putting a few panels on your roof. A home solar power solution is a complete system designed to capture sunlight and turn it into electricity for your house, giving you a clean, personal power source.
This lets you significantly cut down—or even say goodbye to—your reliance on the utility company. It's like having your very own power plant, silently working for you every sunny day.
Understanding Your Home Solar Power System
Jumping into solar is a big step, but it's one that more and more homeowners are taking. It's a smart way to lower those monthly electric bills, secure a reliable power source, and seriously reduce your carbon footprint.
The momentum is undeniable. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), the U.S. shot past five million solar installations in 2024. Even more impressive? That number is expected to double by 2030. This isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift as people realize solar is a solid financial move, not just an eco-friendly one.
graph TD
A[5 Million Installations (2024)] --> B{Projected Growth};
B --> C[10 Million Installations (by 2030)];
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#ccf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
Many people think solar is just about the panels, but that's only part of the story. A true solar solution is a finely tuned system where several critical parts work together seamlessly to bring power into your home.
The Core Components of Your Solar Solution
To really get how solar works, you need to know what each piece of the puzzle does. Every component has a specific job in the journey from raw sunlight to the usable electricity that powers your coffee maker, charges your phone, and keeps the lights on.
A complete home solar system is more than just panels; it’s an integrated ecosystem designed to generate, convert, and manage clean energy tailored to your household’s specific needs.
Let's break down the essential gear that makes up a typical home solar setup. Think of these as the key players on your home's new energy team.
Key Components of a Home Solar Power System
Here’s a quick overview of the essential parts that make up a typical residential solar energy solution.
| Componente | What It Does | Por qué es importante |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Capture sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity through the photovoltaic effect. | These are the "engines" of your system, responsible for all energy production. Their efficiency determines your system's output. |
| Inverter | Converts the DC electricity from the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity. | AC power is the standard form of electricity used by your home's appliances and the utility grid. |
| Racking/Mounting | Securely fastens the solar panels to your roof, holding them in place and at the optimal angle. | Proper mounting ensures the safety, longevity, and maximum sun exposure for your panels. |
| Battery Storage (Optional) | Stores excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night or during a power outage. | A battery provides energy independence, backup power, and maximizes your use of the solar energy you produce. |
Each of these components is vital. From the panels that do the heavy lifting to the inverter that makes the power usable, they all work in concert to deliver clean, reliable energy right where you need it.
Decoding Your Solar System Options
Picking a solar power solution for your home isn’t a one-size-fits-all kind of deal. The right setup for you really boils down to your energy goals, where you live, and how much you want to break away from the traditional power grid. Getting a handle on the three main types of systems is the first, most important step toward finding that perfect match.
A good way to think about it is to picture the utility grid as a huge, shared community bank for electricity. How you decide to interact with this "bank" is what really defines your solar system. Let's break down the options.
pie
title Solar System Types
"Grid-Tied" : 70
"Hybrid" : 25
"Off-Grid" : 5
The Grid-Tied System: Your Connection to the Grid
By far, the most common and straightforward choice for residential solar is the grid-tied system. As the name implies, this setup connects your solar panels directly to the public utility grid.
Think of it like having a special savings account with the power company. When your panels are cranking out more electricity than your home is using, you "deposit" that extra power into the grid. Later, when you need more power than you're generating (like at night), you simply "withdraw" it back. This back-and-forth is called net metering.
- Best For: Homeowners in cities or suburbs with reliable grid access who are mainly looking to slash their electricity bills.
- Key Feature: It hinges on net metering policies, which give you financial credit for the excess energy you contribute to the grid.
- Limitation: Here's the catch—during a power outage, grid-tied systems automatically shut down for safety. So, if the grid goes down, so do you.
This infographic shows a typical installation, a key step toward achieving lower energy bills with a solar investment.
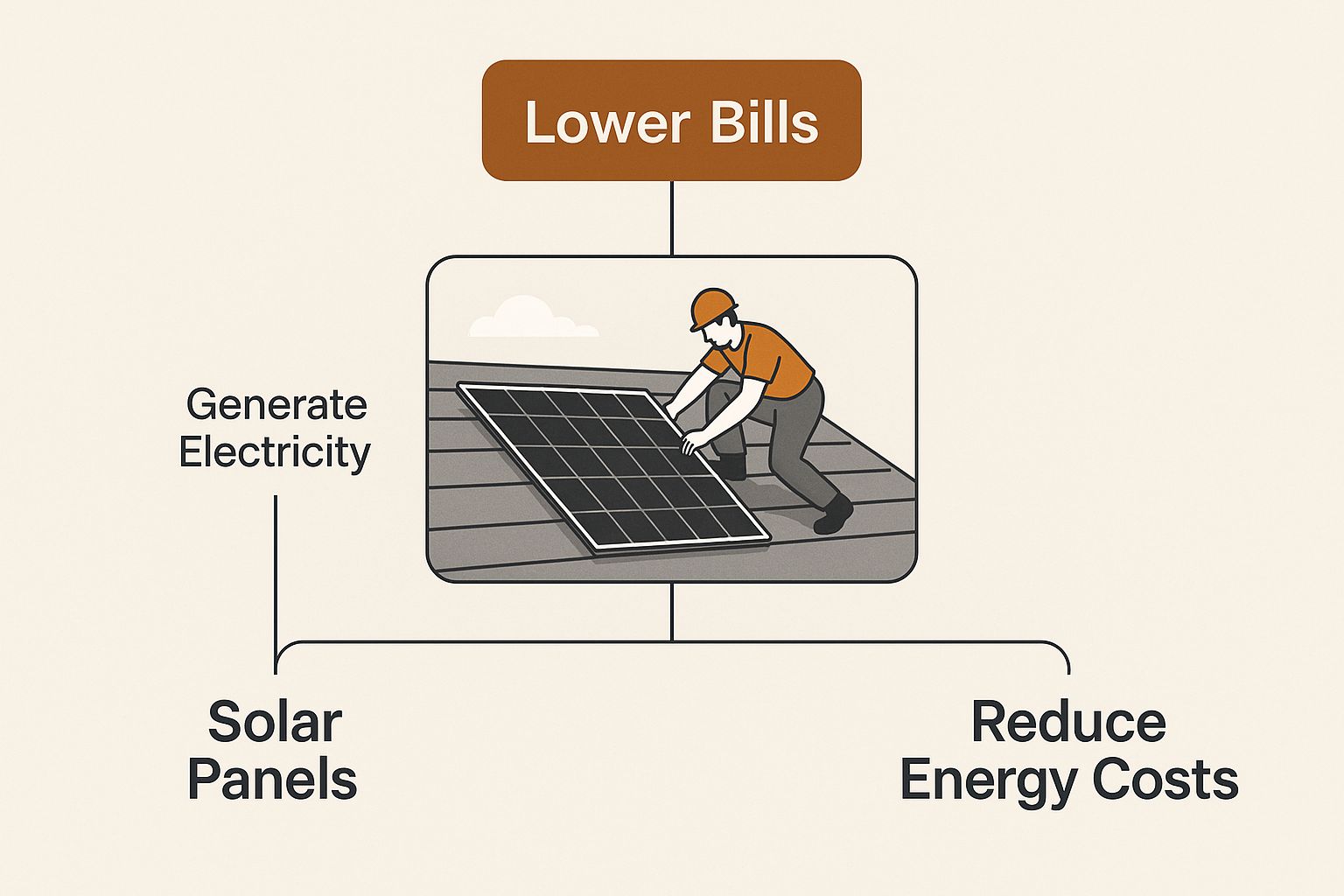
This image really gets to the heart of why so many homeowners go solar—to cut down on those relentless utility costs by making their own clean energy.
The Off-Grid System: Complete Energy Independence
For anyone dreaming of true energy freedom, an off-grid system severs the connection to the utility company entirely. It's the go-to solution for remote properties where hooking up to the grid is either physically impossible or financially crippling.
Sticking with our bank analogy, going off-grid means you are the bank. You generate all your own power, and just as importantly, you have to store it yourself. This demands a serious battery storage system to save the energy your panels collect during the day for use at night or on those inevitable cloudy days.
An off-grid lifestyle demands hands-on energy management. You're in charge of your entire power supply, constantly balancing what you generate, what you store, and what you use.
Living off-grid is a significant commitment. It means a larger upfront investment in batteries and a more mindful approach to how you use electricity, but the reward is total independence.
The Hybrid System: The Best of Both Worlds
A hybrid system gives you a powerful middle ground, blending the reliability of the grid with the security of battery backup. It's quickly becoming the most popular and flexible option for homeowners.
Imagine a hybrid setup as having both a checking account tied to the grid and a private, high-yield savings account—that's your battery. You can pull from the grid whenever you want, but you also have your own energy reserve tucked away for emergencies.
Key benefits of a hybrid setup include:
- Backup Power: When the grid fails, your battery kicks in seamlessly, keeping the lights on and essential appliances running.
- Maximized Savings: You can store extra solar energy in your battery instead of sending it all back to the grid. This is a huge advantage if your utility has low net metering rates.
- Greater Control: You get to decide when to use your stored energy, which lets you sidestep those pricey peak electricity rates and take real control of your power costs.
Choosing the right system involves more than just the technology; the quality of the components themselves is critical. To dive deeper, you should check out our guide on how to choose the best solar panels for your home.
While the residential solar market has its ups and downs, its overall growth trajectory remains strong. For instance, the U.S. residential solar sector added a solid 1,106 MWdc of new capacity in the first quarter of 2025. Even though that's a dip from the previous year, it proves the industry's resilience in the face of economic shifts and policy changes. Every new installation helps build a more reliable and decentralized energy future.
How Big of a Solar System Do I Actually Need?
Before you can even think about panels and inverters, you need to figure out the right-sized system for your home. It's a bit like buying an air conditioner—you wouldn't put a unit designed for a small apartment in a huge house and expect it to work. Getting the size right means you’ll generate enough power to cover your bills without wasting money on a system that’s bigger than you need.
The first step is a little detective work, and your best clue is your monthly utility bill.
Your electric bills are a treasure map, showing exactly how much power your family uses. Look for your consumption measured in kilovatios-hora (kWh). This is the number that matters most. To get a really accurate picture, grab your bills from the last year, add up the total kWh, and divide by 365. That gives you your average daily energy consumption, the starting point for everything else.
It's All About the Sun in Your Area
Once you know how much power you use, the next question is how much you can realistically make. This all comes down to the amount of good, strong sunlight your roof gets, a concept installers call horas punta de sol.
Now, a "peak sun hour" isn't just any old hour the sun is up. It’s an hour where the sun's intensity hits a specific benchmark: 1,000 watts of energy per square meter. So, if your town gets five peak sun hours, it doesn't mean you only get five hours of daylight. It means the total solar energy you receive all day long is equal to five hours at that peak intensity.
This Global Solar Atlas map gives you a great visual of how this varies.
As you can see, places in the Southwest are swimming in solar energy, getting far more intense sunlight (higher kWh/m²) than the Northeast. This has a massive impact on how much electricity a single solar panel can produce in a day.
The Simple Math to Find Your System Size
Okay, now that you have your daily energy use and a rough idea of your local peak sun hours, you can do a quick calculation to estimate your ideal system size. The formula is surprisingly simple and gives you a solid starting point before you even talk to a professional.
Your Daily kWh Use / Peak Sun Hours = Required System Size in kW
Let's make this real. Say your family uses about 30 kWh of electricity per day, and you live in a place that gets around 5 peak sun hours.
Just plug it into the formula: 30 kWh / 5 hours = 6 kW. This tells you that a 6-kilowatt (kW) solar system should be just about right to cover your daily energy needs. This back-of-the-napkin math is incredibly useful for gut-checking the quotes you'll get from installers.
To give you a better feel for what this means, here are some typical system sizes based on household energy use.
| Household Type | Average Daily Use (kWh) | Typical System Size (kW) |
|---|---|---|
| Small Condo/Apartment | 15 – 20 kWh | 3 – 4 kW |
| Mid-Sized Family Home | 25 – 35 kWh | 5 – 8 kW |
| Large Family Home | 40 – 50+ kWh | 8 – 12+ kW |
| Home with EV/Pool | 50 – 70+ kWh | 10 – 15+ kW |
This little chart helps connect the dots between your kWh usage and the actual size of the system you might see on a proposal.
Don't Forget to Plan for the Future
Finally, a truly smart solar plan doesn't just look at today—it looks ahead. Your life isn't static, and your energy needs will likely change. Are you dreaming of buying an electric vehicle in a few years? Thinking about finally installing that pool or switching to an electric heat pump?
Big-ticket items like these can seriously increase your electricity consumption. It’s a great idea to bring up these future plans with your solar installer. They can help you design a system that either has a little extra capacity built-in from day one or is designed in a way that makes it easy to add more panels down the road. A little foresight ensures your solar power solution for home will keep up with your life for years, not just for today.
The Financials of Going Solar
When you start looking into solar power for your home, the conversation always comes back to one thing: money. It’s crucial to stop thinking of solar panels as a simple appliance purchase and start seeing them for what they really are—a long-term investment in your home and your financial future.
Let's break down the upfront costs, the incredible long-term savings, and the valuable incentives that shape the financial journey of a solar homeowner.
The initial price tag for a solar system can feel a bit steep, but it helps to know exactly what you’re paying for. The final cost is influenced by a few key factors, but the two biggest drivers are always tamaño del sistema y equipment quality. A larger home with higher energy needs will require a bigger, more expensive system, and opting for premium, high-efficiency panels will also increase that initial number.
On average, a typical residential solar setup in the U.S. runs somewhere between $18,000 and $20,000 before any incentives are factored in. But that's just the starting point.
This investment is becoming more accessible every year, thanks to a steady drop in solar panel prices over the last decade. It’s a big reason why, since 2021, solar has become the number one source of new electricity generation across the globe. This isn't just a niche trend; it’s a worldwide shift that's reshaping energy policy and proving solar's financial muscle.
Calculating Your Return on Investment
While that initial number is important, the real financial story is in the return you get over time. The most obvious and immediate benefit? A huge drop in your monthly electricity bill. Many homeowners see the savings from day one, and some manage to wipe out their utility bill almost completely.
The next big metric to watch is the solar payback period. This is simply the amount of time it takes for your energy savings to completely cover the initial cost of your system. For most U.S. homeowners, that payback period lands somewhere around 10 años. Once you hit that breakeven point, every single kilowatt-hour of electricity your panels produce for the rest of their 25+ year lifespan is pure savings in your pocket.
Think of it this way: you are essentially pre-paying for decades of electricity at today's fixed price, completely shielding yourself from the unpredictable and ever-increasing rates charged by the utility company.
And the benefits don't stop with your monthly bills. Solar adds real, tangible value to your property. Study after study has shown that homes with an owned solar system sell for a premium. Potential buyers see those panels as a major upgrade that guarantees lower living costs for years to come.
Unlocking Powerful Financial Incentives
This is where the numbers get really exciting. Financial incentives are the game-changers that can dramatically slash the net cost of your system and shorten your payback period.
The single most impactful incentive available is the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This is a big one: it allows you to deduct a whopping 30% of your system's total cost directly from your federal taxes. On a $20,000 system, that’s a $6,000 credit, instantly bringing your net cost down to just $14,000.
gantt
title Solar System Cost Breakdown ($20,000 example)
dateFormat X
axisFormat %S
section Initial Cost
Gross Cost :0, 20000
section After Incentives
Federal ITC (30%) :0, 6000
Net Cost :6000, 20000
But the savings don't stop at the federal level. Many states and even local utility companies offer their own programs to make the deal even sweeter. These can include:
- Créditos fiscales estatales: Some states offer their own tax credits on top of the federal ITC, letting you double-dip on savings.
- Reembolsos en efectivo: These are upfront rebates from your state or utility that directly reduce the initial purchase price.
- Incentivos basados en el rendimiento (PBI): In some areas, you can get paid for the actual amount of solar energy you produce, creating an ongoing revenue stream.
Understanding Your Financing Options
Worried about the upfront cost? You don't need a pile of cash sitting around to make the switch. There are several financing paths available, each with its own advantages.
A solar loan is a popular choice. It lets you finance the system over time while still owning it from day one. This is key because it means you're the one who gets to claim all the valuable tax credits and incentives.
If you'd rather avoid an upfront cost altogether, options like solar leases and Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) are worth exploring. With these models, a third-party company installs and maintains the panels on your roof at little to no cost to you. In return, you pay them a fixed monthly rate for the solar power you use—a rate that's typically lower than what the utility charges. While you won't own the system, you still get the benefit of cheaper, cleaner electricity. If you're weighing your options, you might be interested in our article on the differences between a solar lease vs a PPA.
Choosing the Right Solar Equipment
Picking the right hardware for your solar setup is a bit like casting the lead actors in a play—the performance, lifespan, and even the final look of your system all hinge on the quality of the gear you choose. Just like building a custom computer, you can go for top-of-the-line components for maximum power, or you can find that sweet spot between performance and price.
It all starts with the most visible part of your system: the solar panels. Not all panels are built the same, and getting a handle on the three main technologies is your first big step toward a smart decision.
Comparing Solar Panel Technologies
The type of solar panel you go with directly affects how much electricity your system can squeeze from the sun and what it will look like on your roof. Each one has its own strengths, depending on what you value most—whether that’s getting every possible watt from a small roof or finding the most wallet-friendly option.
Let's unpack the key differences to help you decide which is right for you.
When you're comparing your options, it really comes down to balancing efficiency, cost, and how much space you have to work with. Think of it as a trade-off: higher efficiency often means a higher upfront cost but better performance in a smaller footprint.
Comparación de tecnologías de paneles solares
| Panel Type | Efficiency | Cost | Lifespan | Best For |
| :— | :— | :— | :— |
| Monocristalino | 17-22%+ (Highest) | Higher | 25-40 Years | Homeowners with limited roof space who want maximum power generation and a sleek, uniform look. |
| Policristalino | 15-17% (Good) | Lower | 25-35 Years | Budget-conscious homeowners with ample roof space who want a reliable, cost-effective panel. |
| Capa fina | 10-13% (Lower) | Varies | 10-20 Years | Niche applications like RVs or flexible surfaces; less common for standard residential rooftops. |
So, what does this all mean in the real world? Monocrystalline panels, with their classic all-black look, are the high-performers. They're made from a single, pure silicon crystal, which makes them the most efficient. You simply need fewer of them to get the job done.
Polycrystalline panels, which you can spot by their blue, almost marbled appearance, are made from melted-down silicon fragments. The process is simpler and less expensive, making them a great budget-friendly choice, even if they aren't quite as efficient. If you’ve got plenty of sunny roof space, they offer fantastic value.
Understanding the Brains of the System: Inverters
If solar panels are the heart of your system, the inverter is the brain. It handles one of the most critical jobs of all: converting the direct current (DC) electricity your panels generate into the alternating current (AC) that your home appliances and the utility grid actually use.
The two main types you'll come across are string inverters and microinverters.
- Inversores de cadenas: This is the classic, time-tested approach. It works by connecting a group (or "string") of panels to a single, central inverter. It's a reliable and cost-effective workhorse, but it has one major catch: the entire string's output is dragged down by its weakest link. If even one panel is shaded, the production of all the others in that string takes a hit.
- Microinversores: This more modern technology puts a small inverter on the back of every single panel. This simple change means each panel operates independently, pushing out its maximum power regardless of what its neighbors are doing. If one panel gets shaded, the rest keep cranking. They cost more, but they are perfect for complicated roofs or homes with occasional shading.
Completing the Solution with Solar Batteries
A solar battery is what takes your system from a simple money-saver to a genuine energy independence tool. It acts like a personal energy reservoir, storing the extra solar power your panels produce during the day so you can tap into it whenever you want—at night, on a cloudy day, or, most importantly, during a power outage.
Adding a battery gives you true energy freedom. You get to use more of your own clean power instead of selling it back to the grid for pennies, and you get the priceless peace of mind that comes with knowing your lights will stay on when the grid goes down.
The global push for residential energy is impossible to ignore. In 2024, an estimated 600 GW of new solar capacity was installed worldwide, bringing the global total to over 2,2 teravatios (TW). This incredible growth is what continues to make solar technology more affordable and accessible for homeowners everywhere.
When looking at specific solar-powered products, even simple additions like the Wilson LED Solar Wall Lamp can offer practical, efficient outdoor lighting. Of course, understanding the full financial picture is key; our guide to solar panel system installation cost can help you get a clear idea of the investment.
Your Common Solar Questions Answered

Thinking about going solar is exciting, but it’s completely normal to have a few lingering questions. It’s a big decision! To help you feel confident, we've gathered some of the most common questions we hear from homeowners and answered them directly.
Let’s tackle the practical side of owning a solar system—from how long it will last and what upkeep is needed, to what happens when the power goes out. Getting these details straight can be the final piece of the puzzle as you figure out the best solar power solution for your home.
How Long Do Solar Panels Last?
The question of durability and maintenance comes up a lot. The good news is that today's solar panels are built like tanks. Most manufacturers back their panels with a performance warranty of De 25 a 30 años, which is a testament to how reliable they are. And even after three decades, they don't just switch off; they simply produce a little less power than they did on day one.
As for maintenance, it's surprisingly hands-off. For most people, regular rain showers are all it takes to keep the panels clean. If you live in a drier, dustier area, a quick rinse with a garden hose a few times a year will do the trick. A professional check-up every few years isn't a bad idea either, just to make sure everything is in tip-top shape.
High-quality solar panels are a long-term asset designed for decades of reliable, low-maintenance energy production, making them a true "set it and forget it" home upgrade.
This incredible lifespan means your investment keeps paying you back for years and years, offering both energy savings and total peace of mind.
Will I Have Power During a Blackout?
This is a big one, and the answer comes down to one thing: your system’s design. A standard grid-tied solar system has to shut down when the grid goes down. It's a mandatory safety measure designed to protect the utility workers who are out there fixing the power lines.
If you want to keep the lights on during an outage, you’ll need to add a solar battery to your system. This addition turns your setup into a hybrid solution. The battery stores the extra solar energy your panels produce, creating a personal power reserve you can tap into anytime—especially during a blackout. It’s the key to true energy independence and security.
Does My Roof Have to Face South?
It's a common myth that you need a perfect, south-facing roof to go solar. While that’s often considered the "ideal" setup in the Northern Hemisphere, it's far from the only option. In reality, east- and west-facing roofs are fantastic for solar panels.
Here’s a quick breakdown of why other directions work so well:
- East-Facing Panels: They soak up the powerful morning sun, which is great for powering your home right as your day gets going.
- West-Facing Panels: These are champs at capturing late afternoon sunlight, perfectly timed for when energy use often peaks as everyone gets home from work or school.
A good solar installer won’t just eyeball it. They'll do a full analysis of your roof's unique pitch, orientation, and any potential shade to map out the most productive system for your specific home.
How Does Solar Affect My Home Value?
Adding a solar power system isn't just about cutting your electricity bills; it's also a smart way to boost your property value. Study after study has shown that homes with an owned solar energy system sell for more money than comparable homes without one.
Think about it from a buyer’s perspective. They see solar panels as a high-value, built-in feature that promises lower utility costs for years to come. This makes your home stand out in the market, often leading to a quicker sale at a better price. The exact boost in value can depend on your location, but one thing is clear: solar is an investment that pays you back every month and again when you sell.
Ready to explore a custom solar power solution for your home? The experts at Energía radiante are here to design a system that fits your energy needs and financial goals, helping you achieve energy independence with top-quality equipment and professional installation. Start your journey to a brighter, cleaner energy future today. Learn more at Radiant Energy.




