Picture this: a life where you're the one in charge of your power. No more utility bills, no more worries about grid failures. Just you, your home, and the sun. Using solar panels for off grid living isn't just a fantasy; it's a practical way to achieve true energy independence and build a genuinely sustainable lifestyle.
Your Path to Energy Independence with Solar

Going off-grid with solar is a major shift. It's about more than just equipment—it's about becoming resilient and self-sufficient. Whether you're planning a remote cabin getaway, looking for a reliable alternative to a spotty power grid, or going all-in on reducing your environmental impact, solar is the foundation.
The first step isn't buying panels. It’s understanding that an off-grid system is your own private power station. It has to be designed to handle everything you throw at it, from the coffee pot in the morning to the lights on a stormy winter night. There’s no utility company to back you up.
The Core Components of Your System
When you break it down, a well-designed off-grid solar setup really relies on four key pieces of hardware working together seamlessly.
graph TD
A[Solar Panels<br>Generate DC Power] --> B(Charge Controller<br>Manages Power Flow);
B --> C{Battery Bank<br>Stores Energy};
C --> D(Inverter<br>Converts DC to AC);
D --> E[Home Appliances<br>Use AC Power];
subgraph Your Off-Grid System
A
B
C
D
end
- Solar Panels: These are your power generators. They catch sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity. Simple as that.
- Charge Controller: Think of this as the system's brain. It carefully manages the flow of power from the panels to the batteries, preventing overcharging which can seriously shorten their lifespan.
- Battery Bank: This is your energy savings account. It stores all the power generated during the day so you can use it at night or when the sun isn't shining. It's what makes 24/7 power a reality.
- Inverter: This is the final, crucial step. It takes the DC power stored in your batteries and converts it into the alternating current (AC) electricity that almost all of your home appliances need to run.
A lot of people think off-grid living means giving up modern comforts. That's just not true anymore. With smart planning and the right size system, an off-grid home can power just about everything a grid-tied home can. The main difference is you become much more aware of how and when you use your energy.
This growing desire for energy freedom is showing up in the numbers. The global off-grid solar market was valued at USD 3.11 billion y se espera que ascienda a USD 10.11 billion by 2035. That’s a huge jump, and it tells you everything you need to know about where things are headed. You can get more details on the off-grid solar PV panel market from this report by Spherical Insights.
Planning Your Off-Grid Solar Journey
Building an off-grid system that you can actually rely on takes careful planning. Unlike a grid-tied setup, there's no safety net if you get your calculations wrong. Your system has to be sized perfectly for your specific power needs, your location's weather patterns, and your family's lifestyle.
To help you get started, here's a quick look at the major phases you'll go through when setting up your own off-grid solar project.
Quick Overview of an Off-Grid Solar Project
This table breaks down the entire process into manageable stages, from initial brainstorming to long-term care.
| Project Phase | Key Objective | Main Components/Tasks |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Assessment | Figure out exactly how much power you use daily. | Auditing appliances, calculating watt-hours, and planning for seasonal highs and lows. |
| System Design | Size all components based on your energy needs. | Calculating the right size for your solar array, battery bank, inverter, and charge controller. |
| Installation | Physically assemble and wire the entire system. | Mounting the panels, connecting all the components, and safely setting up the battery bank. |
| Operation & Maintenance | Keep the system running efficiently for years. | Monitoring your energy usage, cleaning panels regularly, and checking on battery health. |
Getting these stages right is the key to a successful, stress-free off-grid experience. This guide will walk you through each one, giving you the practical steps you need to take along the way.
Sizing Your System Starts with Sizing Up Your Life

Before you can even dream about what solar panels for off grid living look like on your roof, you have to get brutally honest about how much power you actually use. This is the single most important step, and it’s the one where most people go wrong.
Guessing here is a recipe for disaster. Get it wrong, and you'll end up with a system that either can't keep the lights on or cost you thousands more than it should have. So, let’s forget the generic online calculators for a minute and do a proper, real-world energy audit.
Living off-grid demands a much deeper understanding of your consumption than you ever needed when tied to a utility company. We’re going to figure out your exact power needs, watt by watt, to build a system that works for your life—in the dead of winter and on the sunniest summer day.
Your Personal Energy Audit
Grab a notepad or fire up a spreadsheet. Your first mission is to walk through your home and list every single thing that uses electricity. And I mean everything.
Don't just list the big stuff like the fridge and the TV. Get granular. Note the coffee maker, the laptop chargers, the tiny nightlight in the hallway, the electric toothbrush. Be meticulous.
For every item on your list, you need to find two things:
- Wattage: How much power it draws when running. This is usually on a small label on the back of the device or its power cord.
- Daily Run Time: An honest estimate of how many hours (or fractions of an hour) you use it each day. A TV might be on for 4 hours, but a microwave might only run for 10 minutes (0.17 hours).
Now, just multiply these two numbers together for each device: (Wattage) x (Hours Used Per Day) = Daily Watt-hours (Wh). Add up the results for everything on your list, and you'll have your total daily energy demand. This is the magic number your entire system design will hinge on.
Taming the "Phantom Loads"
Ever notice the little red light on your TV when it’s “off”? Or the clock on your microwave? Those are phantom loads—devices that are constantly sipping electricity, even in standby mode.
Individually, they seem insignificant. But together, these hidden energy drainers can account for a shocking 5-10% of your total electricity usage. For an off-grid system, that’s a huge deal. You need to account for them. A simple tool like a Kill A Watt meter can be invaluable here; just plug it in between the wall and the appliance to see exactly what it's drawing.
The best off-grid systems are built on a solid foundation of data. Taking the time to do this energy audit right is the smartest investment you can make. It’s what prevents the gut-wrenching feeling of running out of power on a cloudy day or the sting of overspending on a system you didn’t need.
An Example: A Small Homestead's Energy Budget
Let's see what this looks like in the real world. Here’s a sample worksheet for a small, energy-conscious homestead, breaking down the daily load to get a clear target.
| Appliance | Quantity | Wattage (Watts) | Daily Run Time (Hours) | Daily Energy (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kitchen | ||||
| Refrigerator | 1 | 150 | 8 | 1200 |
| Coffee Maker | 1 | 1000 | 0.25 | 250 |
| Microwave | 1 | 1200 | 0.15 | 180 |
| Living Area | ||||
| LED Lights | 6 | 10 | 5 | 300 |
| Laptop | 1 | 65 | 4 | 260 |
| TV | 1 | 100 | 3 | 300 |
| Bedroom | ||||
| LED Lights | 2 | 10 | 2 | 40 |
| Phone Chargers | 2 | 5 | 2 | 20 |
| Utility | ||||
| Water Pump | 1 | 500 | 0.5 | 250 |
| Daily Total | 2800 Wh |
This audit gives us a daily target of 2,800 Wh, or 2.8 kilowatt-hours (kWh). With this number in hand, you can confidently start planning your solar array and battery bank.
For a deeper dive, our complete guide on how to calculate solar panel needs has more tips and formulas. Just remember to think about seasonal changes—you’ll use more lights in the winter—to make sure your system is ready for anything the year throws at it.
Choosing the Right Hardware for Your System

Okay, you've done the math and have a solid energy budget. Now for the exciting part: picking the hardware that will become the beating heart of your off-grid power station.
Making the right choices here is absolutely critical. The components you select will directly impact your system's reliability, how much power you actually get, and how long it all lasts. Each piece has a job to do, and I'll walk you through the real-world pros and cons so you can build a setup that truly fits your needs.
Selecting Your Solar Panels: Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline
Your first big decision is what kind of solar panels for off grid living to get. The two most common kids on the block are monocrystalline and polycrystalline. The best one for you really boils down to your climate, how much space you have, and your budget.
pie
title Solar Panel Market Share
"Monocrystalline" : 65
"Polycrystalline" : 30
"Other (Thin Film, etc)" : 5
-
Monocrystalline Panels: You can spot these by their uniform black color. They're made from a single, pure silicon crystal, which makes them more efficient. If you're working with a small roof or a tight spot on the ground, their ability to produce more power per square foot is a huge win. They also tend to have a slight edge in low-light conditions and on really hot days.
-
Polycrystalline Panels: These have a blue, almost mosaic-like look because they're made from multiple silicon fragments melted together. They aren't quite as efficient, so you'll need a bit more surface area to get the same power output. The trade-off? Their manufacturing process is simpler, which usually makes them easier on the wallet upfront.
Think of it this way: for a small cabin in an area with a lot of overcast days, the extra efficiency of monocrystalline panels is a smart investment. But if you have a big, sunny field for a ground-mount system where space is no object, the initial cost savings of polycrystalline panels might make more sense.
The Critical Role of the Charge Controller
If your solar panels are the generators, then the charge controller is the brain of the operation. This little box sits between your panels and your batteries, and its job is to regulate the flow of power to prevent overcharging. This one component is hands-down the most important thing for protecting your expensive battery bank and making it last.
You'll run into two main types:
-
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): This is the older, simpler tech. It basically acts like a switch, turning the connection to the batteries on and off very quickly to manage the charge. They’re cheap and they work fine for small, basic setups where squeezing out every last watt isn't the main goal.
-
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT): This is where the real magic happens. MPPT controllers are far more advanced and can take the high-voltage power from your panels and efficiently convert it to the lower voltage your batteries need. This process lets them capture way more energy.
An MPPT charge controller can boost your system's energy harvest by up to 30%, especially in colder weather or on partly cloudy days. Yes, they cost more upfront, but that efficiency gain often means you can get the power you need with fewer panels, paying for the upgrade in just a couple of years.
For almost any serious off-grid project, an MPPT controller is the only way to go. The efficiency boost is just too significant to pass up, ensuring you’re harvesting every possible watt from your array.
Demystifying Battery Technology
Your battery bank is your energy savings account—it stores power so you can have lights on at night and run your coffee maker on a rainy day. This is usually the single most expensive part of an off-grid system, so the technology you choose will have a huge effect on performance, maintenance, and long-term costs.
The main choice is between old-school lead-acid and modern lithium-ion batteries. While lead-acid was the go-to for decades, lithium (specifically Fosfato de litio y hierro, or LiFePO4) has become the clear winner for most off-grid solar systems today.
The good news is that the global push for renewable energy is making this technology more affordable than ever. The cumulative installed photovoltaic (PV) capacity worldwide has already blown past 2,2 teravatios (TW). While most of that is grid-tied, the sheer scale of production has driven down costs for everyone, including those of us building off-grid.
Finally, don't forget the inverter! This is what turns the DC power stored in your batteries into the AC power that your appliances actually use. Choosing the right one is just as important as your panels and batteries. To get a better handle on this, check out our guide explaining qué son los inversores solares and how to select the perfect one for your system.
Off Grid Battery Technology Comparison
Choosing a battery isn't just about the price tag you see today; it's about the total cost and performance over a decade or more. This table breaks down the key differences to help you decide which battery is the right long-term investment.
| Característica | Flooded Lead-Acid (FLA) | Sealed Lead-Acid (AGM) | Lithium-Ion (LiFePO4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coste inicial | Bajo | Moderado | Alta |
| Lifespan (Cycles) | 500 – 1,000 | 700 – 1,500 | 3,000 – 7,000+ |
| Maintenance | High (Requires regular watering) | Ninguno | Ninguno |
| Depth of Discharge | 50% | 50% | 80-100% |
| Eficacia | ~80% | ~85% | 95%+ |
| Long-Term Value | Fair | Good | Excellent |
While it's tempting to go with lead-acid because of the lower initial price, their short lifespan, maintenance headaches, and limited usable capacity mean you'll probably replace them two or even three times before a single lithium bank wears out. For anyone serious about long-term off-grid living, the higher upfront cost of lithium pays for itself with incredible reliability and far better value over the life of the system.
Putting It All Together: A Practical Assembly Guide
You've done the research and have a pile of carefully chosen hardware ready to go. Now for the exciting part: bringing your off-grid solar system to life. While the final, high-voltage connections are strictly a job for a licensed electrician, knowing the assembly process inside and out is crucial. This knowledge puts you in the driver's seat of your project, ensuring safety is always the top priority and giving you a real appreciation for how each part contributes to your personal power plant.
This is where your paper plans become a physical reality. You'll be making some big decisions on the ground—where to place your panels, how to route the wiring, and where to build the secure heart of your system: the power center.
This infographic breaks down the core stages of the physical installation.
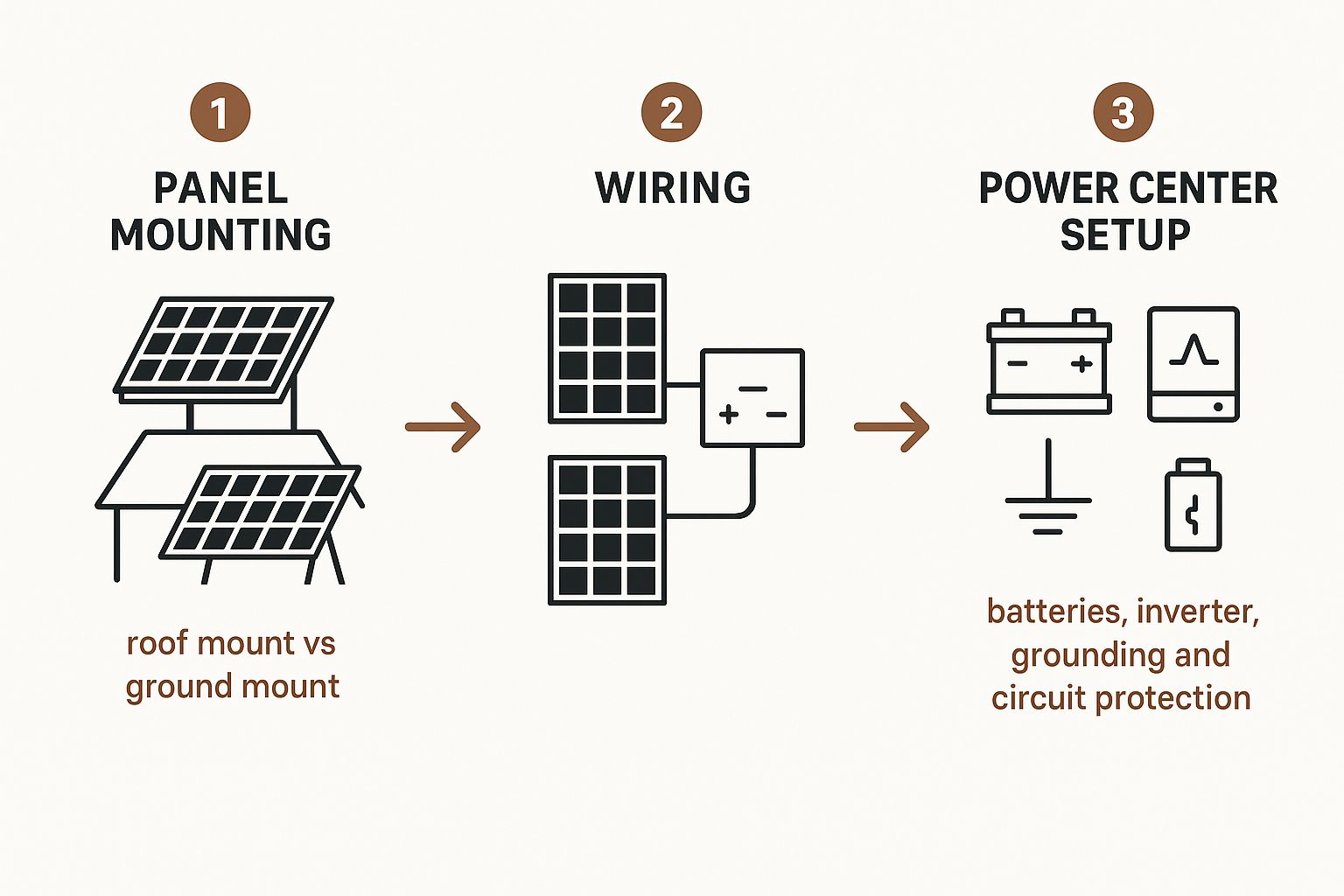
Think of it as the journey your power will take: from the panels where it's collected, through the wiring, to the central hub where it's managed and stored, and finally, out to your home.
Panel Mounting: Ground vs. Roof
One of the first hands-on decisions you'll make is where to mount your solar panels. This choice has a ripple effect on everything from your system's efficiency to how you'll handle maintenance down the road. Both options have their pros and cons, and the right answer really depends on your property.
-
Roof Mounts: This is the go-to for most people, and for good reason. It puts unused roof space to work, leaving your yard clear. A roof-mounted array also keeps your expensive panels up and away from ground-level hazards and accidental bumps.
-
Ground Mounts: If you're looking for peak performance, ground mounts offer unbeatable flexibility. You can orient the panels to the perfecto angle and direction for maximum sun exposure—something your roofline might not allow. Plus, clearing snow or performing routine checks is a whole lot easier (and safer) when your feet are firmly on the ground.
If you’re blessed with a large, clear, south-facing roof, a roof mount is probably the most direct path. But for anyone trying to squeeze every last watt out of their system, the performance boost from a perfectly angled ground mount can be well worth it.
Consejo profesional: Don't ever cut corners on grounding. A properly grounded system is your first and best line of defense against lightning strikes and electrical faults. This isn't just a recommendation; it's a non-negotiable safety measure that protects your home and your investment.
Setting Up the Power Center
Your inverter, charge controller, and battery bank form the central nervous system of your off-grid setup, and they need a safe, dedicated space to live. This "power center" should be located in a protected, well-ventilated area like a garage, a sturdy shed, or a custom-built enclosure.
Ventilation is especially important for battery health and safety, as some types can release gases during heavy charging cycles. The location also needs to be secure, keeping the components safe from accidental contact and shielded from extreme temperatures that can hammer battery performance and shorten their lifespan. A clean, organized power center makes future monitoring and maintenance a breeze.
This is also home base for your critical safety gear. You absolutely must have circuit protection, like fuses and breakers, at key points in the system. These devices are your fail-safes. They automatically cut the flow of electricity during a short circuit or overload, preventing catastrophic equipment failure or even a fire. For a deeper dive into the entire build, our guide on the solar panel installation process covers every step in detail.
By truly understanding the logic behind panel placement, wiring paths, and setting up a secure power center, you gain the confidence to oversee your installation effectively. This ensures your investment in solar panels for off grid living is not only powerful and efficient but, most importantly, safe for many years to come.
Living with Your Off Grid Solar System
https://www.youtube.com/embed/2MYrL6M9q58
So, your off-grid solar system is installed, the last wire is connected, and the power is on. This is where the real adventure begins. You're not just flipping a switch anymore; you're living in sync with your own personal power plant. It's less about technical know-how and more about developing a new rhythm—an awareness of the energy you generate and the energy you use.
This lifestyle is becoming more and more mainstream as the technology gets better. The off-grid solar market, valued at about USD 2.74 billion, is expected to skyrocket to around USD 9.23 billion by 2035. This boom isn't just happening because of initiatives to power remote areas, but because these systems are more dependable than ever. You can dig into the numbers yourself and explore the off-grid solar market growth at Market Research Future.
Mastering Your Energy Flow
Your system monitor is about to become your best friend. Think of it as the dashboard for your home's power station, giving you a live look at what you’re producing and what you’re using. Getting comfortable reading it is probably the single most important skill for living happily off-grid.
You'll quickly start to see the patterns. On a clear, sunny morning, your panels will be cranking out way more power than you need, and all that extra juice goes right into your batteries. That's your "power surplus" window. On the flip side, during a cloudy afternoon or after the sun goes down, you'll see your home pulling its power directly from that stored energy.
The secret to thriving off-grid is surprisingly simple: use your power when you're making it. Get into the habit of running the big-ticket appliances—the vacuum, washing machine, or even power tools—in the middle of a sunny day. This one change takes a massive load off your batteries, helping them last longer and making sure you have plenty of power saved for the night.
This simple shift in thinking changes you from someone who just pays a bill into an active energy manager. It's one of the most satisfying parts of using solar panels for off grid living.
A Practical Maintenance Schedule
One of the best things about an off-grid system is how little day-to-day work it requires. It's low-maintenance, but not no-maintenance. A few simple, regular checks are all it takes to keep everything running at peak performance for years to come. You don't need to become a solar technician, just an observant owner.
Here’s a realistic schedule you can actually stick to:
| Frequency | Task | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| Quarterly | Clean Solar Panels | Dust, pollen, and general grime can slash your panel output by 5-15%. A quick rinse with a hose and a soft brush on a cool, cloudy morning is usually enough to bring them back to full strength. |
| Semi-Annually | Inspect Battery Terminals | Give your battery terminals a once-over, looking for any corrosion (that white, crusty buildup), especially on lead-acid types. Make sure the connections are snug. If you see gunk, a wire brush and a paste of baking soda and water will clean it right up. |
| Annually | Check Wiring and Connections | Do a quick visual sweep of all the wiring. Look for any signs of chewing from critters or damage from the weather. At your power center, double-check that all connections are tight and there are no signs of scorching or overheating. |
Following a simple routine like this isn't just about maintenance. It's about protecting your investment and ensuring the lights stay on, no matter what. It’s a tiny bit of effort for total energy freedom.
Common Questions About Off-Grid Solar
Once you've done the math on your power needs and started picking out gear, the "what if" questions naturally start to bubble up. It's one thing to design a system on paper, but it's another to live with it day in and day out. Let's walk through some of the most common questions we get from people making the jump to solar panels for off grid living.
How Many Backup Days Should I Plan For?
This is all about "days of autonomy"—how long your system can carry you through a stretch of bad weather with zero sunshine. Think of it as your energy insurance policy.
For most people, aiming for 3 to 5 days of backup power is a solid target. That's usually enough to weather a typical storm front or a few gloomy, overcast days without having to drastically cut your power usage.
However, if you're in a region with long, dark winters or if your setup powers something absolutely critical, you'll want to aim higher. Sizing your battery bank for 5 to 7 days of autonomy provides a much more robust safety net and some serious peace of mind.
This chart gives you a clear picture of how battery capacity translates to backup days, assuming you use about 4 kWh of energy daily.
As you can see, a bigger battery bank directly buys you more security when the sun decides not to show up for a while.
Can I Start Small and Expand My System Later?
Yes, you absolutely can. In fact, it's a very practical way to manage the initial cost. But—and this is a big but—you have to plan for it from the get-go.
The trick is to oversize the brains of your system right from the start. Your charge controller and inverter are the core components that dictate the maximum size of your system. If you want to double your panels and batteries in a couple of years, you need an inverter and charge controller that can handle that future capacity today.
Think of your inverter and charge controller as the foundation of your power system. It costs a bit more to pour a foundation for a two-story house, but it's a whole lot cheaper than tearing out the old one when you decide to build up.
Spending a little extra on these core electronics upfront will save you a massive headache and thousands of dollars down the road. It makes expansion a simple matter of adding more panels and batteries, not replacing the most expensive parts of your setup.
What Happens to Excess Power I Generate?
On those perfect, blazing sunny days, your panels might generate more power than your batteries need. So where does it all go? Is it wasted?
Not at all. A modern off-grid system handles this automatically. Once your batteries are topped off, your solar charge controller simply stops sending power to them. It effectively tells the solar panels for off grid living to take a break.
This process, called regulation, prevents overcharging, which is crucial for protecting your batteries from damage and ensuring they last as long as possible. The potential extra energy is just left unharvested. It's a completely normal and essential function that keeps your entire system healthy and stable.
Ready to take control of your energy future? At Energía radiante, we specialize in designing and installing high-quality, reliable solar solutions that empower you to live life on your own terms. Explore our off-grid systems and get a personalized quote today at radiantenergysolar.com.