At its heart, solar energy is simply the light and heat beaming down from the sun. It’s the most plentiful energy source we have on Earth, and for decades, we've been perfecting the technology to capture that power for our homes and businesses.
The Power of the Sun Explained
Imagine the sun as a colossal nuclear reactor floating in space, constantly radiating immense amounts of energy in every direction. When we talk about what is solar energy, we're really talking about our clever ways of catching a tiny sliver of that cosmic power and putting it to good use right here on the ground.
Best of all, this process is clean. Capturing sunlight doesn't create the greenhouse gas emissions that come from burning fossil fuels, making it a powerful tool in our move toward cleaner energy.
The growth in solar has been nothing short of astonishing. Since 2014, the amount of power we generate from the sun has exploded, reaching over 2,129 terawatt-hours (TWh) globally by mid-2025. That means solar now accounts for about 8% of the world's electricity—a massive jump for a technology that really only started its mainstream boom about eleven years ago. You can find more details on this incredible solar energy growth on goldmansachs.com.
Chart: Growth of Global Solar Electricity Generation (TWh)
graph TD
A[Year 2014: ~180 TWh] --> B[Year 2020: ~844 TWh];
B --> C[Year 2023: ~1,600 TWh];
C --> D[Mid-2025 (Projected): 2,129+ TWh];
style A fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style C fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style D fill:#f9f,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
Two Primary Ways to Capture Solar Energy
We generally use two different methods to grab sunlight and convert it into something we can use. Each one works differently and serves a distinct purpose, but understanding both gives you a great picture of how solar technology operates.
-
Photovoltaic (PV) Systems: This is what most people picture when they think of solar. Those familiar panels on rooftops use special semiconductor materials to convert sunlight directly into electricity. It’s a fascinating process called the photovoltaic effect, where sunlight literally knocks electrons loose, creating a flow of electricity.
-
Solar Thermal Systems: This method isn't about making electricity; it’s about capturing heat. These systems use collectors—often tubes or flat plates—to absorb the sun's warmth. That heat is then transferred to water, making it perfect for your home's hot water supply, heating a swimming pool, or even powering industrial applications.
By using these two approaches, we can transform raw sunlight into a reliable and sustainable power source, cutting down on our dependence on the old-school energy grid.
How Solar Panels Create Usable Electricity
Ever looked up at a solar panel and wondered how that sleek, dark rectangle actually powers a home? It’s a pretty amazing process, turning pure sunlight into the electricity we rely on for everything from our coffee makers to our laptops. The magic behind it all is a scientific principle called the photovoltaic effect.
Let's break it down. Sunlight isn't just a steady glow; it’s made up of countless tiny energy packets called photons. When these photons shower down onto a solar panel, they hit the solar cells inside. These cells are usually made from silicon and are layered to create an electric field, kind of like the positive and negative ends of a battery.
Turning Sunlight into Electrical Current
When a photon strikes a silicon cell, it gives an electron a jolt of energy, knocking it loose. Imagine a cue ball breaking a rack of billiard balls—that initial impact gets everything moving. The built-in electric field in the solar cell then grabs these free-roaming electrons and shoves them all in one direction.
This organized, one-way flow of electrons is exactly what an electric current is.
The photovoltaic effect is the direct conversion of light into electricity at the atomic level. Some materials exhibit a property known as the photoelectric effect that causes them to absorb photons of light and release electrons. When these free electrons are captured, an electric current results.
While a single solar cell doesn't produce much power on its own, a standard solar panel strings together 60 or 72 cells. Working as a team, they generate a meaningful amount of direct current (DC) electricity anytime the sun is out.
This is a great visual of how the whole "sun-to-power" journey works.
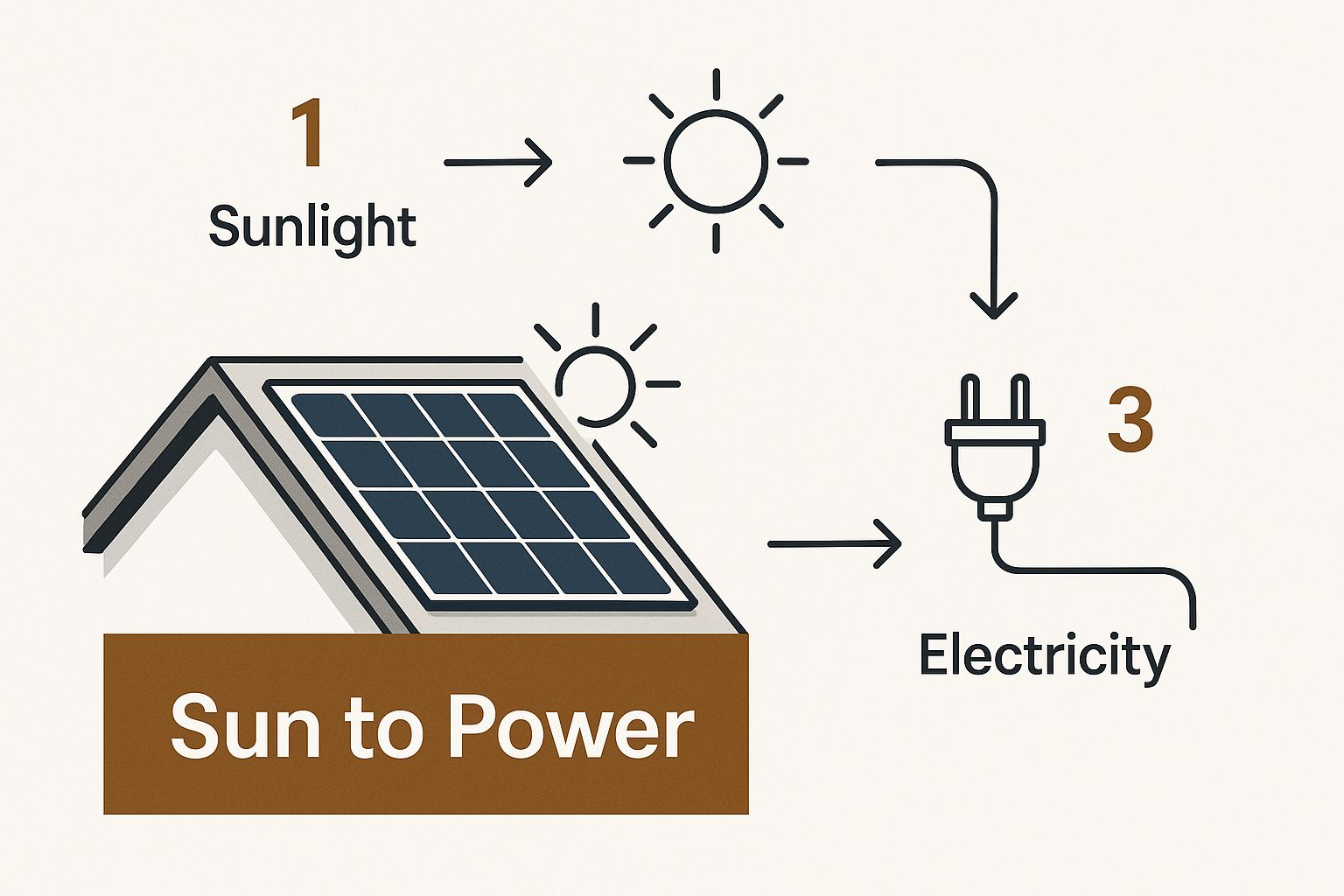
As you can see, it all starts with the sun's rays and ends with usable power for your home, all thanks to the clever design of each solar cell.
Making the Electricity Ready for Your Home
There's one more crucial step. The DC electricity from your panels isn't quite ready for your home's appliances, which run on alternating current (AC). That's where a device called an inversor comes in. The inverter is the real workhorse of your solar setup, instantly converting that DC power into home-ready AC power.
From there, the electricity is good to go, powering anything you plug into an outlet. You can get an even more detailed explanation of how solar panels work for homes if you'd like to dive deeper.
The entire sequence—from photon to light switch—happens in a flash, silently and cleanly. Once you understand how home solar works, you can really appreciate just how straightforward and effective it is for generating your own power right from the roof.
The Key Parts of a Home Solar Power System
When you think of a solar energy system, the first thing that probably comes to mind is the sleek panels on a rooftop. But that's only part of the story. A complete home solar setup is actually a collection of high-tech components, all working in perfect sync to turn sunshine into the electricity that powers your life.
Let's break down what each piece does, so you can see how raw sunlight becomes usable power for your home.
It all begins with the solar panels. These are made up of many smaller photovoltaic cells, and their one job is to catch sunlight and kickstart the energy conversion process. You can think of them as the system's collectors, gathering the free, raw fuel source—sunlight—and turning it into direct current (DC) electricity.
But there's a catch. The DC power from your panels isn't what your refrigerator or TV uses. Your home's appliances run on alternating current (AC). That's where the most important piece of the puzzle comes in.

The Inverter: The Brains of the Operation
En inversor is the real heart of your solar system. This device takes the DC electricity generated by the panels and converts it into the AC electricity your home can actually use. Without it, all that captured sunlight would be useless. There are three main types you'll encounter:
- Inversores de cadenas: The classic, most common option. It links a group (or "string") of solar panels together and sends all their DC power to one central inverter box. It’s a simple, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
- Microinversores: This approach puts a small, individual inverter on the back of every single panel. They convert electricity right at the source, which is a huge advantage if a panel gets shaded or covered in leaves—it won't drag down the performance of the entire system.
- Optimizadores de potencia: Think of this as a middle ground. Small "optimizers" are attached to each panel to condition the DC power before sending it to a main string inverter. This gives you many of the panel-level benefits of microinverters but often at a slightly lower price point.
Racking and Monitoring Systems
Of course, those panels need to be attached to your roof securely. That's the job of the racking and mounting hardware. This is the rugged metal framework that holds everything in place, engineered to handle decades of wind, snow, and rain. A proper installation here is non-negotiable for the safety and lifespan of your system.
Finally, how do you know if it's all working? A monitoring system gives you a live look at your system's output. Through a simple app on your phone or a website, you can see exactly how much power you're generating in real-time. It's a great way to watch your savings add up and spot any potential issues right away.
To give you a better sense of how these pieces fit together financially, here's a quick look at what they do and how much they typically contribute to the total cost.
Components of a Typical Home Solar System
| Componente | Función principal | Typical % of Total System Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Capture sunlight and convert it to DC electricity. | 25% – 35% |
| Inverter | Converts DC electricity from panels into usable AC electricity. | 10% – 15% |
| Racking/Mounting | Securely fastens the solar panels to the roof or ground. | 8% – 12% |
| Monitoring System | Tracks and reports real-time energy production. | 1% – 3% |
| Installation/Labor | The professional labor to design and install the system. | 10% – 20% |
| Permits & Fees | Required local permits, inspections, and utility connection fees. | 5% – 10% |
| Balance of System | All other parts like wiring, conduits, and safety disconnects. | 5% – 10% |
As you can see, every part has its place and its price.
Each component, from the panels grabbing the light to the inverter making it useful, is essential. Understanding their roles is the first step to making a smart investment in your home's energy future.
When you're ready to look at the numbers, it helps to see a full financial picture. You can dive deeper into the coste de instalación de un sistema de paneles solares to understand how all these hardware, labor, and permitting costs come together. The more you know about what goes into a system, the more you'll appreciate the clean energy it produces for years to come.
Harnessing the Sun's Heat with Solar Thermal
When people ask, "what is solar energy," minds usually jump straight to those familiar rooftop panels that make electricity. But there’s another powerful way to tap into the sun's energy, one that focuses purely on its warmth: solar thermal technology. It’s a surprisingly simple and incredibly effective way to cut your energy bills.
Ever left a garden hose out in the sun and been blasted by surprisingly hot water? Solar thermal systems work on that exact same principle, just on a much more sophisticated and efficient scale. Instead of making electricity, their one job is to capture heat.
This heat is perfect for one of the biggest energy hogs in any home: the water heater. A solar thermal system can handle the bulk of your hot water needs for showers, laundry, and dishes, giving your conventional water heater a serious break. For most families, heating water is one of the top energy expenses, right behind air conditioning and heating.
How Solar Thermal Collectors Work
At the heart of the system are the solar thermal collectors. Their job is to absorb as much solar radiation as possible and transfer that warmth into a fluid. This heated fluid is then piped to a storage tank, ready to use.
There are two main designs you'll see:
-
Flat-Plate Collectors: These are the workhorses of residential solar water heating. They look like a shallow, insulated box with a dark absorber plate inside, all protected by a glass cover. A fluid (usually a water/glycol mix) flows through tiny tubes in the plate, soaking up the sun's heat as it passes through.
-
Evacuated Tube Collectors: This design is a bit more high-tech. It uses a row of glass tubes, each with an absorber tube inside a vacuum-sealed space. That vacuum is a fantastic insulator, meaning very little heat escapes. This makes them highly efficient, giving them an edge in colder climates or on cloudy days.
A properly sized solar water heating system can provide 50% to 80% of a household's hot water for free. That’s a direct hit to your utility bills and a big step away from relying on natural gas or propane.
The beauty of solar thermal lies in its directness and simplicity. It's a reliable, long-lasting investment that does one thing exceptionally well. By focusing solely on heating water, it offers a practical and proven way to put the sun's natural warmth to work in your home.
Financial and Environmental Reasons to Go Solar
So, what’s driving the huge wave of people switching to solar? When you get right down to it, the decision almost always boils down to two powerful motivators: saving money and helping the planet. It’s this one-two punch of real financial returns and a positive environmental footprint that makes solar such a compelling choice for homeowners today.

From a financial standpoint, the most obvious and exciting perk is watching your monthly electric bill shrink. When you start generating your own power, you naturally buy far less from the utility company. For many homeowners, this means drastically lower bills, and in some cases, you might eliminate them altogether.
Maximizing Your Financial Return
Beyond the immediate bill savings, a whole ecosystem of incentives exists to make the initial investment much easier to swallow. Government and local programs are in place specifically to encourage people like you to adopt solar.
Here’s a look at the most common ones:
- Federal Tax Credits: This is a big one. The federal solar tax credit lets you deduct a huge chunk of your system's total cost directly from what you owe on your federal taxes. Think of it as a massive, government-backed discount on your entire project.
- Net Metering: This is a brilliant billing setup that essentially turns your utility meter into a two-way street. When your panels produce more electricity than you're using, that excess power flows back to the grid. The utility company credits you for that power, which you can then draw on at night or on cloudy days.
- State and Local Rebates: Don't forget to look locally! Many states, cities, and even individual utility companies offer their own cash-back rebates or extra tax breaks to sweeten the deal even further.
The global solar industry was valued at $189.5 billion in 2022 and is projected to skyrocket to $607.8 billion by 2030. That incredible growth is happening for a reason. On average, a residential solar system can slash a household's energy bills by 20% to 50%.
Chart: Global Solar Market Growth Projection
graph LR
A[2022: $189.5 Billion] --> B[2030 (Projected): $607.8 Billion];
style A fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
style B fill:#bbf,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px
When you add it all up, these programs transform a solar installation from a simple home expense into a legitimate financial investment. For those looking to support larger projects, various renewable energy grants are also available to help get things off the ground.
Protecting the Planet from Your Rooftop
Of course, the environmental side of the equation is just as powerful. Every single kilowatt-hour of clean electricity your panels generate is one less that has to be produced by burning fossil fuels. This has a direct and immediate impact on shrinking your carbon footprint and fighting back against climate change.
Making the switch means you're actively creating cleaner air for your community. It helps reduce our country's reliance on finite resources like coal and natural gas, which in turn fosters greater energy independence and helps build a more stable, sustainable power grid for everyone.
Figuring out the best financial route, like understanding the difference between https://radiantenergysolar.com/solar-leasing-vs-ppa/, allows you to align your personal budget with your sustainability goals. At the end of the day, putting solar panels on your roof is a tangible way to invest in the kind of future you want to see.
The Global Shift Toward Solar Power
Not long ago, solar energy felt like a niche technology for early adopters. Today, it’s a full-blown global powerhouse, fundamentally changing how we generate electricity across the planet. This isn't just a slow-moving trend; it's an explosive shift driven by plummeting costs, incredible gains in efficiency, and a shared global push for cleaner power.
The numbers alone tell a staggering story. By the end of 2024, the world’s collective solar capacity blew past 2,2 teravatios (TW). To put that in perspective, that’s up from 1.6 TW just a year before. In 2024 alone, a record-shattering 600 GW of new solar came online, with China responsible for installing nearly 60% of that new capacity. For a deeper dive into the data, check out the IEA-PVPS Global PV Markets Snapshot.
The Momentum of a Mainstream Movement
This incredible worldwide momentum proves solar isn't just a viable alternative anymore—it's fast becoming the primary source of new energy in many parts of the world. The energy landscape is changing before our eyes, and you can read more about solar's increasing dominance as an electricity source, where it’s now outpacing traditional fuels for new installations. This isn't a fad; it's a validation of solar as a smart, secure investment for the future.
Investing in solar today means joining a massive, mainstream movement. It's a practical step toward energy independence and a direct contribution to a cleaner, more resilient global power grid.
Governments everywhere are throwing their weight behind this transition, rolling out policies that encourage everything from massive desert solar farms to the panels on your neighbor’s roof. When you understand this bigger picture, you see that putting solar on your own home is about more than just lowering your electric bill. It's about being part of a powerful story of progress and innovation.
Common Questions About Solar Energy
As you start to explore solar energy, a lot of practical questions naturally come to mind. It’s a big decision for your home, and you deserve clear, straightforward answers. We've gathered some of the most common questions we hear from homeowners to help you get the facts.
Let's cut through the noise and give you the essential info you need to feel confident about your energy future.
How Long Do Solar Panels Actually Last?
This is usually the first thing people ask, and for good reason—it’s a long-term investment. You'll be happy to know that modern solar panels are built like tanks. They're designed to withstand decades of sun, wind, rain, and snow.
Most top-tier manufacturers back their panels with a performance warranty guaranteeing they'll still produce at least 80-90% of their original power after 25 años. In reality, many systems keep chugging along, generating clean electricity long after that warranty period is over.
Do Solar Panels Still Work On Cloudy Days?
Yes, they absolutely do. It's a common myth that solar panels need blazing hot, direct sunlight to work. While they definitely hit their peak performance on bright, sunny days, they don't just switch off when the clouds roll in.
The key is that panels run on light, not heat. Even on a completely overcast day, your system can still generate 10% to 25% of its typical output from diffused sunlight. That’s still power you don’t have to buy from the utility company.
Graph: Solar Panel Output by Weather Condition
pie
title Solar Panel Output on an Overcast Day
"Typical Output (10-25%)" : 25
"Potential Output Loss" : 75
What Happens During a Power Outage?
This is a really important one to understand. A standard solar system that's connected to the grid is designed to automatically shut down during a power outage. This is a crucial safety measure that prevents your panels from sending electricity back into the grid and potentially harming utility workers making repairs.
But what if you want to keep the lights on? This is where a solar battery storage system comes in. By pairing your panels with a battery, you can store the excess energy you generate and use it to power your home when the grid goes down. It’s the key to true energy independence.
What Is the Real Cost of a Home Solar System?
The final price tag for a home solar system can vary quite a bit, and it really depends on your specific situation. The main factors that influence the cost are:
- System Size: The number of panels you need to offset your home's energy consumption.
- Equipment Quality: The brands and efficiency ratings of your panels and inverter.
- Your Location: Labor costs and local permit fees can differ from one city to the next.
- Available Incentives: Big ticket items like the federal solar tax credit and local rebates can dramatically lower your net cost.
While the upfront cost is what most people focus on, it's more accurate to see it as an investment. Over time, most solar systems pay for themselves in electricity savings, and then continue to provide you with free, clean power for many years to come.
Ready to get a clear answer on what solar could cost—and save—for your specific home? Energía radiante offers custom solar designs and transparent pricing to help you make the best decision. Get your free, no-obligation solar quote today by visiting https://radiantenergysolar.com.



